what is the world’s leading renewable energy source used to produce electricity?
At-a-glance
- Renewable energy is the fastest-growing energy source in the United States, increasing 42 percent from 2010 to 2020 (up 90 percentage from 2000 to 2020).
- Renewables fabricated up nearly twenty percent of utility-scale U.S. electricity generation in 2020, with the majority coming from hydropower (7.3 percent) and wind power (8.4 percent).
- Solar generation (including distributed), which made up 3.3 percent of total U.Due south. generation in 2020, is the fastest-growing electricity source.
- Globally, renewables fabricated up 29 percent of electricity generation in 2020, much of it from hydropower (16.8 percent).
- A record amount of over 256 GW of renewable power capacity was added globally during 2020.
- Renewable ethanol and biodiesel transportation fuels made up more than 17 percent of full U.S. renewable energy consumption in 2020, a decrease from recent years, probable due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Renewable Supply and Demand
Renewable energy is the fastest-growing free energy source globally and in the United states.
Globally:
- Nigh 11.2 per centum of the free energy consumed globally for heating, power, and transportation came from modernistic renewables in 2019 (i.e., biomass, geothermal, solar, hydro, wind, and biofuels), up from 8.7 pct a decade prior (see figure below).
- Renewables fabricated up 29 percent of global electricity generation by the end of 2020. Led past wind power and solar PV, more than 256 GW of capacity was added in 2020, an increase of almost x percent in total installed renewable power capacity.
The International Energy Agency notes that the development and deployment of renewable electricity technologies are projected to proceed to be deployed at record levels, but government policies and fiscal support are needed to incentivize even greater deployments of make clean electricity (and supporting infrastructure) to give the world a chance to accomplish its net nada climate goals.
Estimated Global Renewable Energy Share of Total Final Energy Consumption (2009-2019)
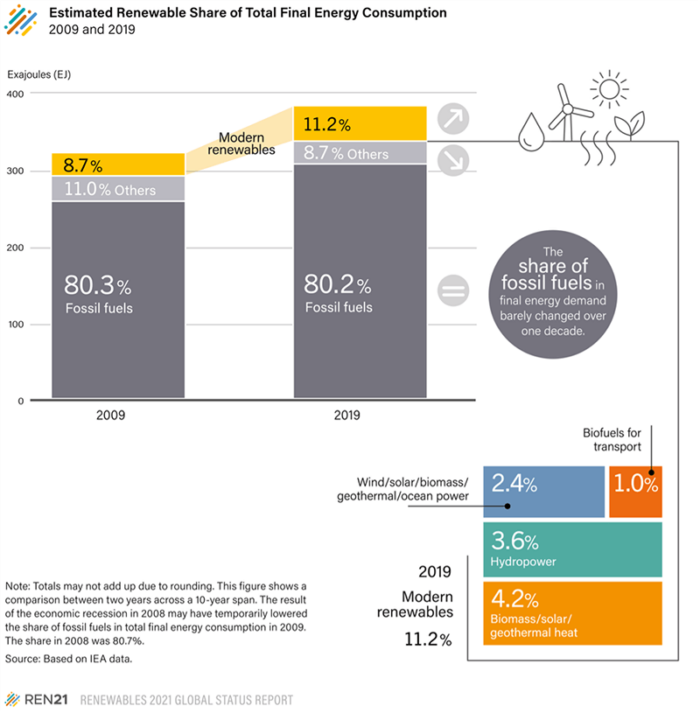
In the United States:
- Almost 5 percent of the energy consumed across sectors in the U.s.a. was from renewable sources in 2020 (11.six quadrillion Btu out of a total of 92.nine quadrillion Btu). U.S. consumption of renewables is expected to grow over the next 30 years at an boilerplate annual charge per unit of 2.4 percent, higher than the overall growth rate in energy consumption (0.5 percent per yr) under a business-as-usual scenario.
- Renewables fabricated up xix.8 percent of electricity generation in 2020, with hydro and air current making up the majority. That's expected to rise to 35 percent past 2030. Most of the increase is expected to come up from wind and solar. Not-hydro renewables take increased their share of electric power generation from less than 1 percentage in 2005 to over 12.5 percent at the end of 2020 while demand for electricity has remained relatively stable.
In the transportation sector, renewable fuels, such equally ethanol and biodiesel, have increased significantly during the past decade. However, slower growth (i.e., 0.half-dozen – 0.7 percent annual growth) is expected out to mid-century.
In the industrial sector, biomass makes up 98 percent of the renewable energy apply with roughly threescore percentage derived from biomass wood, 31 percentage from biofuels, and about 7 percent from biomass waste matter.
Uncertainty about federal tax credits (eastward.thousand., Renewable Fuel Standard), California's Low Carbon fuel standard, fuel prices, and economical growth will influence the footstep of U.S. renewable energy source evolution.
Renewable Energy Drivers
Factors affecting renewable free energy deployment include marketplace atmospheric condition (east.g., price, variety, proximity to demand or transmission, and resource availability), policy decisions, (e.g., revenue enhancement credits, feed-in tariffs, and renewable portfolio standards) every bit well as specific regulations. Almost all countries had renewable energy policy targets in place at the end of 2020.
Businesses with sustainability goals are also driving renewable energy development by building their own facilities (e.g., solar roofs and wind farms), procuring renewable electricity through power purchase agreements, and purchasing renewable energy certificates (RECs).
Current of air and solar renewable energy technologies have seen substantial price declines over the by decade. Between 2010 and 2019, the cost of utility-scale solar photovoltaics fell 82 per centum, and the toll of onshore wind fell 39 percent. Increased demand and procurement requires more than of these technologies to exist manufactured and developed, causing reduced costs due to learning and economies of scale, which increases the incentive for additional procurement.
Global weighted average levelized cost of electricity from utility-calibration power generation technologies, 2010 and 2019
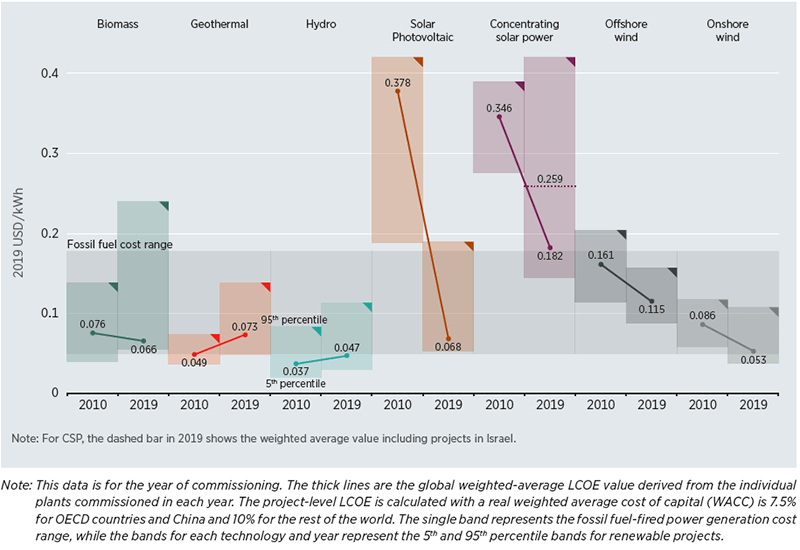
Policy Drivers
Two federal tax credits take encouraged renewable energy in the United States:
- The production revenue enhancement credit (PTC), get-go enacted in 1992 and later on amended, was a corporate revenue enhancement credit available to a wide range of renewable technologies including wind, landfill gas, geothermal, and small hydroelectric. For eligible technologies, the utility received a 2.ii ¢/kWh ($22/MWh) credit for all electricity generated during the first ten years of operation. The PTC is currently beingness phased out; at the end of December 2020, the PTC was extended for another twelvemonth at 60 percent of the full credit corporeality, and facilities start construction later on December 31, 2021 volition no longer be able to merits this credit.
- The investment revenue enhancement credit (ITC) is earned when qualifying equipment, including solar hot water, photovoltaics, and small-scale current of air turbines, are placed into service. The credit reduces installation costs and shortens the payback fourth dimension of these technologies. The Consolidated Appropriations Act (2016) extended the ITC for three years, only Congress and so passed a two year filibuster in 2020. It will stage downwards to 10 percentage in 2024 (from 26 pct in 2021).
States offer added incentives, making renewables even easier to implement from a cost perspective.
A renewable portfolio standard requires electric utilities to deliver a sure amount of electricity from renewable or alternative energy sources by a given date. State standards range from modest to ambitious, and qualifying energy sources vary. Some states also include "carve-outs" (requirements that a sure percentage of the portfolio exist generated from a specific energy source, such every bit solar power) or other incentives to encourage the development of detail resources. Although climatic change may not be the prime number motivation behind these standards, they tin can deliver pregnant greenhouse gas reductions and other benefits, including job creation, energy security, and cleaner air. Virtually states let utilities to comply with the renewable portfolio standard through tradeable credits that utilities can sell for boosted acquirement.
In states with a renewable portfolio standard, utilities consider price, intermittency and resource availability in choosing technologies that satisfy this requirement.
In the U.Due south. transportation sector, The Energy Policy Act of 2005 created a Renewable Fuel Standard that required 2.78 percent of gasoline consumed in the United States in 2006 to be renewable fuel.
The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 created a new Renewable Fuel Standard, which increased the required volumes of to 36 billion gallons past 2022, or near 7 percent of expected annual gasoline and diesel fuel consumption to a higher place a business-as-usual scenario.
Types of Renewable Energy
Renewable free energy comes from sources that tin be regenerated or naturally replenished. The main sources are:
- Water (hydropower and hydrokinetic)
- Wind
- Solar (power and hot water)
- Biomass (biofuel and biopower)
- Geothermal (power and heating)
All sources of renewable energy are used to generate electric power. In addition, geothermal steam is used directly for heating and cooking. Biomass and solar sources are too used for space and h2o heating. Ethanol and biodiesel (and to a lesser extent, gaseous biomethane) are used for transportation.
Renewable free energy sources are considered to be zippo (current of air, solar, and h2o), low (geothermal) or neutral (biomass) with regard to greenhouse gas emissions during their operation. A neutral source has emissions that are balanced by the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed during the growing process. However, each source's overall environmental impact depends on its overall lifecycle emissions, including manufacturing of equipment and materials, installation as well as land-use impacts.
Water
Large conventional hydropower projects currently provide the majority of renewable electric ability generation worldwide. With most 1,170 gigawatts (GW) of global capacity, hydropower produced an estimated 4,370 terawatt hours (TWh) of the roughly 26,000 TWh total global electricity in 2020.
The Us is the fourth-largest producer of hydropower afterward People's republic of china, Brazil, and Canada. In 2011, a much wetter than average twelvemonth in the U.S. Northwest, the Usa generated 7.9 percent of its total electricity from hydropower. The Department of Energy has plant that the untapped generation potential at existing U.S. dams designed for purposes other than power production (i.e., water supply, flood control, and inland navigation) represents 12 GW, roughly 15 pct of current hydropower chapters.
Hydropower operational costs are relatively low, and hydropower generates piddling to no greenhouse gas emissions. The main environmental impact is that a dam to create a reservoir or divert h2o to a hydropower plant changes the ecosystem and physical characteristic of the river.
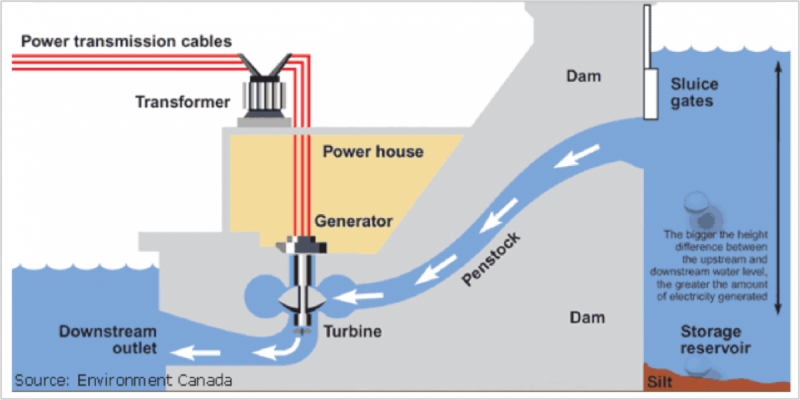
Waterpower captures the free energy of flowing h2o in rivers, streams, and waves to generate electricity. Conventional hydropower plants tin exist congenital in rivers with no water storage (known as "run-of-the-river" units) or in conjunction with reservoirs that store water, which can be used on an as-needed basis. Equally water travels downstream, it is channeled downwardly through a pipage or other intake structure in a dam (penstock). The flowing water turns the blades of a turbine, generating electricity in the powerhouse, located at the base of operations of the dam.
Other Hydroelectric Power Generation
Small hydropower projects, generally less than ten megawatts (MW), and micro-hydropower (less than 1 MW) are less costly to develop and have a lower environmental impact than large conventional hydropower projects. In 2019, the total amount of small hydro installed worldwide was 78 GW. Mainland china had the largest share at 54 percent. China, Italy, Japan, Kingdom of norway and the United States are the top v minor hydro countries by installed capacity. Many countries have renewable energy targets that include the evolution of small hydro projects.
Hydrokinetic electric power, including wave and tidal power, is a grade of unconventional hydropower that captures energy from waves or currents and does not require dam construction. These technologies are in various stages of research, development, and deployment. In 2011, a 254 MW tidal power plant in South Korea began operation, doubling the global capacity to 527 MW. By the cease of 2018, global capacity was virtually 532 MW.
Low-head hydro is a commercially available source of hydrokinetic electric ability that has been used in farming areas for more than than 100 years. Generally, the capacity of these devices is small-scale, ranging from 1kW to 250kW.
Pumped storage hydropower plants use inexpensive electricity (typically overnight during periods of low demand) to pump water from a lower-lying storage reservoir to a storage reservoir located above the power firm for subsequently utilise during periods of elevation electricity demand. Although economically viable, this strategy is non considered renewable since it uses more than electricity than it generates.
Hydroelectric Power Generation
Wind
Wind was the second largest renewable energy source worldwide (after hydropower) for ability generation. Wind ability produced more than than six percent of global electricity in 2020 with 743 GW of global chapters (707.4 GW is onshore). Capacity is indicative of the maximum corporeality of electricity that can be generated when the air current is blowing at sufficient levels for a turbine. Considering the air current is not always blowing, wind farms do not e'er produce every bit much as their capacity. With effectually 290 MW, China had the largest installed capacity of wind generation in 2020. The United states of america, with 122.5 GW, had the second-largest capacity; Texas, Oklahoma, Iowa, and Kansas provide more than half of U.S. current of air generation, with Texas greatly leading all other states in installed capacity, at 27 percent of the U.S. total. In 2019, wind free energy overtook hydropower for the largest share of renewable generation in the U.South., providing 8.4 pct of electricity in 2020.
Although people have harnessed the energy generated past the movement of air for hundreds of years, modern turbines reflect significant technological advances over early windmills and even over turbines from just x years ago. Generating electric power using air current turbines creates no greenhouse gases, but since a wind farm includes dozens or more turbines, widely-spaced, it requires thousands of acres of land. For example, Lone Star is a 200 MW wind farm on approximately 36,000 acres in Texas. Nevertheless, most of the land in between turbines can still be utilized for farming or grazing.
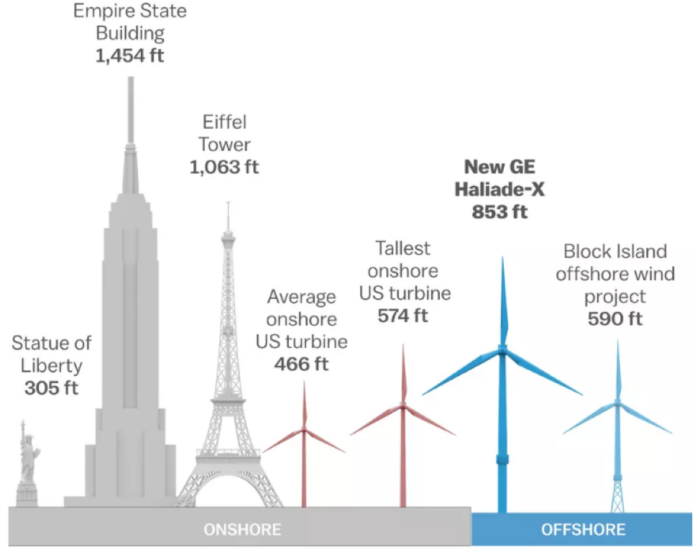
Average turbine size has been steadily increasing over the past xxx years. Today, new onshore turbines are typically in the range of two – 5 MW. The largest production models, designed for off-shore use can generate 12 MW; some innovative turbine models under evolution are expected to generate more than 14 MW in offshore projects in the coming years. Due to higher costs and technology constraints, off-shore capacity, approximately 35.six GW in 2020, is merely a small share (about 5 percent) of total installed wind generation capacity.
Air current Turbine Sizes
Solar
Solar energy resources are massive and widespread, and they can be harnessed anywhere that receives sunlight. The corporeality of solar radiations, also known as insolation, reaching the Earth's surface every 60 minutes is more than all the energy currently consumed by all human activities each year. A number of factors, including geographic location, time of day, and atmospheric condition atmospheric condition, all touch the amount of free energy that can be harnessed for electricity production or heating purposes.
Solar photovoltaics are the fastest growing electricity source. In 2020, effectually 139 GW of global capacity was added, bringing the total to most 760 GW and producing almost three per centum of the world's electricity.
Solar energy can be captured for electricity product using:
- A solar or photovoltaic prison cell, which converts sunlight into electricity using the photoelectric effect. Typically, photovoltaics are plant on the roofs of residential and commercial buildings. Additionally, utilities have constructed big (greater than 100 MW) photovoltaic facilities that require anywhere from 5 to 13 acres per MW, depending on the technologies used. In the United States, non-residential solar (e.g. utility-scale) installations made up 16.7 GW, while residential solar (e.thousand. rooftop) installations made upward xix.1 GW.
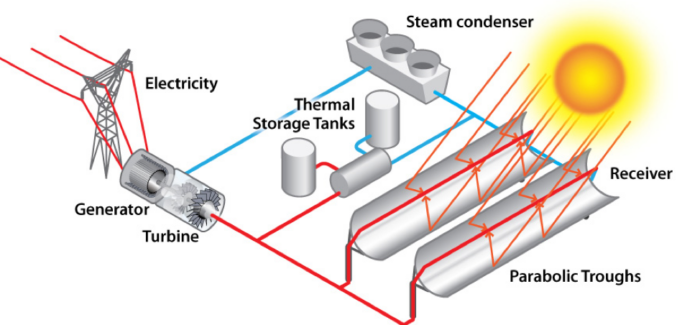
- Concentrating solar power (CSP), which uses lenses or mirrors to concentrate sunlight into a narrow beam that heats a fluid, producing steam to drive a turbine that generates electricity. Concentrating solar power projects are larger-calibration than residential or commercial PV and are oft owned and operated by electrical utilities.
- Although utility-scale CSP plants were in performance long before solar photovoltaics became widely commercialized, solar photovoltaics take largely taken over this market, due to their declining costs. Global CSP capacity grew only ane.6 percent in 2020 to six.2 GW.
Solar hot water heaters, typically found on the roofs of homes and apartments, provide residential hot water by using a solar collector, which absorbs solar energy, that in turn heats a conductive fluid, and transfers the heat to a water tank. Modern collectors are designed to be functional even in cold climates and on clouded days.
Electricity generated from solar free energy emits no greenhouse gases. The main ecology impacts of solar energy come from the use of some hazardous materials (arsenic and cadmium) in the manufacturing of PV and the big amount of land required, hundreds of acres, for a utility-scale solar project.
Concentrating Solar Power
Biomass
Biomass energy sources are used to generate electricity and provide direct heating, and tin be converted into biofuels as a direct substitute for fossil fuels used in transportation. Unlike intermittent wind and solar energy, biomass can be used continuously or according to a schedule. Biomass is derived from wood, waste, landfill gas, crops, and alcohol fuels. Traditional biomass, including waste matter wood, charcoal, and manure, has been a source of free energy for domestic cooking and heating throughout human history. In rural areas of the developing earth, it remains the dominant fuel source. Globally in 2019, bioenergy accounted for about 11.half dozen pct of total energy consumption. The growing utilize of biomass has resulted in increasing international trade in biomass fuels in recent years; wood pellets, biodiesel, and ethanol are the main fuels traded internationally.
In 2020, global biomass electric ability capacity stood at 145 GW, increasing 5.8 percent from the previous year. The U.s. had 16 GW of installed biomass-fueled electric generation capacity. In the United States, well-nigh of the electricity from wood biomass is generated at lumber and paper mills using their ain wood waste matter; in addition, woods waste is used to generate the rut for drying forest products and other manufacturing processes. Biomass waste is mostly municipal solid waste, i.e., garbage, which is burned equally a fuel to run ability plants. On average, a ton of garbage generates 550 to 750 kWh of electricity. Landfill gas contains marsh gas that tin exist captured, processed and used to fuel power plants, manufacturing facilities, vehicles and homes. In the United States, there is currently more than than 2 GW of installed landfill gas-fired generation capacity at more than than 600 projects.
In improver to landfill gas, biofuels can be synthesized from dedicated crops, trees and grasses, agricultural waste matter, and algae feedstock; these include renewable forms of diesel, ethanol, butanol, methane, and other hydrocarbons. Corn ethanol is the near widely used biofuel in the United states. Roughly 39 percentage of the U.S. corn crop was diverted to the production of ethanol for gasoline in 2019, upward from xx percent in 2006. Gasoline with upward to 10 percent ethanol (E10) tin can be used in virtually vehicles without further modification, while special flexible fuel vehicles can use a gasoline-ethanol alloy that has up to 85 per centum ethanol (E85).
Closed-loop biomass, where ability is generated using feedstocks grown specifically for the purpose of energy production, is by and large considered to be carbon dioxide neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion of the fuel was previously captured during the growth of the feedstock. While biomass can avoid the use of fossil fuels, the net event of biopower and biofuels on greenhouse gas emissions will depend on total lifecycle emissions for the biomass source, how information technology is used, and indirect land-use effects. Overall, still, biomass free energy can accept varying impacts on the surround. Forest biomass, for example, contains sulfur and nitrogen, which yield air pollutants sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, though in much lower quantities than coal combustion.
Geothermal
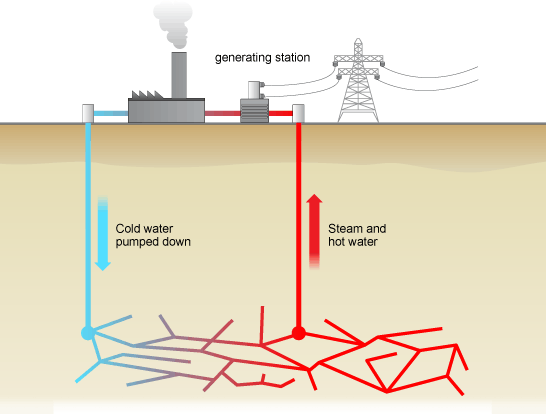
Geothermal provided an estimated 225 TWh globally in 2020, with 97 TWh in the course of electricity (with an estimated xiv.1 GW of capacity) and the remaining half in the class of heat. (Total global electricity generation in 2020 was 26,000 TWh).
In the United States, nearly 17 TWh of geothermal electricity was generated in 2020, making up about 3.4 percentage of non-hydroelectric renewable electricity generation, merely only 0.four pct of full electricity generation. Seven states generated electricity from geothermal free energy: California, Hawaii, Idaho, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon and Utah. Of these, California accounted for 80 percent of this generation.
Traditional geothermal free energy exploits naturally occurring high temperatures, located relatively close to the Globe'southward surface in some areas, to generate electric power and for straight uses such as heating and cooking. Geothermal areas are generally located near tectonic plate boundaries, where in that location are earthquakes and volcanoes. In some places, hot springs and geysers have been used for bathing, cooking and heating for centuries
Generating geothermal electric power typically involves drilling a well, perhaps a mile or ii in depth, in search of rock temperatures in the range of 300 to 700°F. H2o is pumped downwards this well, where it is reheated by hot rocks. Information technology travels through natural fissures and rises upwardly a second well as steam, which can be used to spin a turbine and generate electricity or be used for heating or other purposes. Several wells may accept to be drilled before a suitable i is in place and the size of the resource cannot exist confirmed until after drilling. Additionally, some water is lost to evaporation in this process, then new water is added to maintain the continuous menstruation of steam. Similar biopower and unlike intermittent wind and solar power, geothermal electricity tin can be used continuously. Very minor quantities of carbon dioxide trapped below the World'due south surface are released during this process.
Enhanced geothermal systems utilise advanced, often experimental, drilling and fluid injection techniques to augment and expand the availability of geothermal resources.
Geothermal Power Station
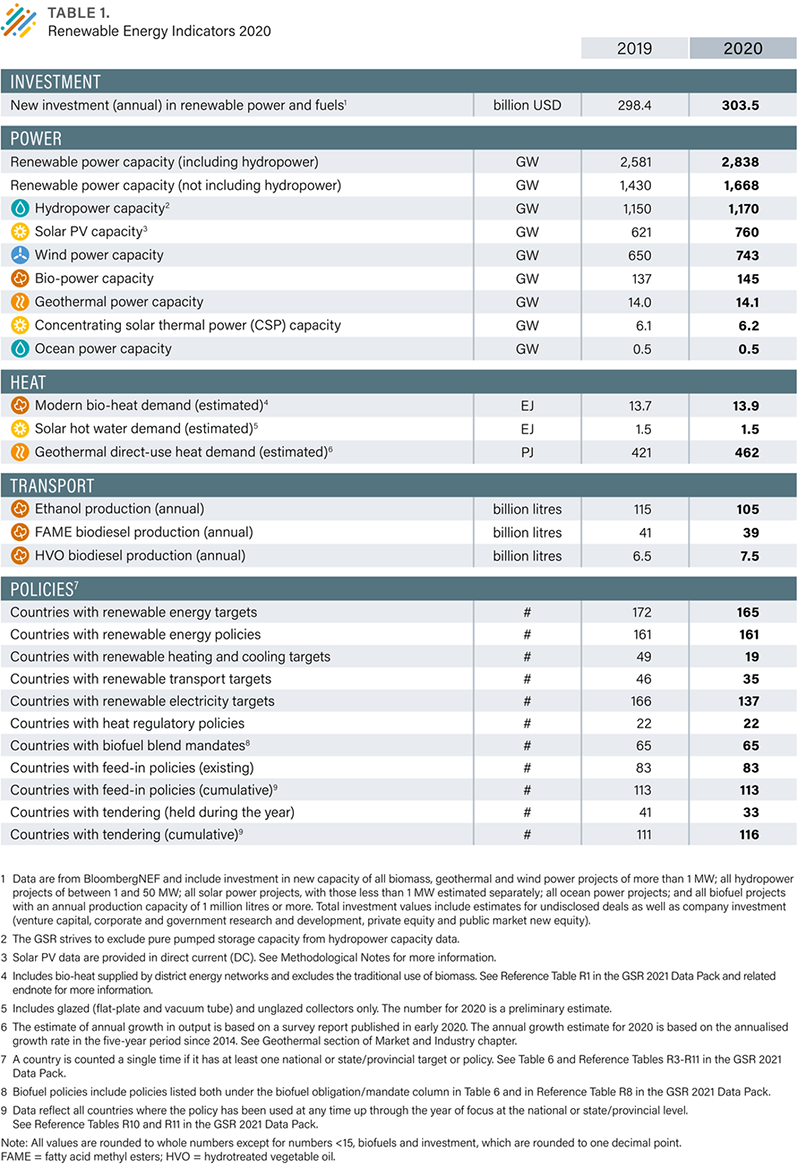
Renewable Energy Indicators, 2020
U.South. Renewable Resource Availability
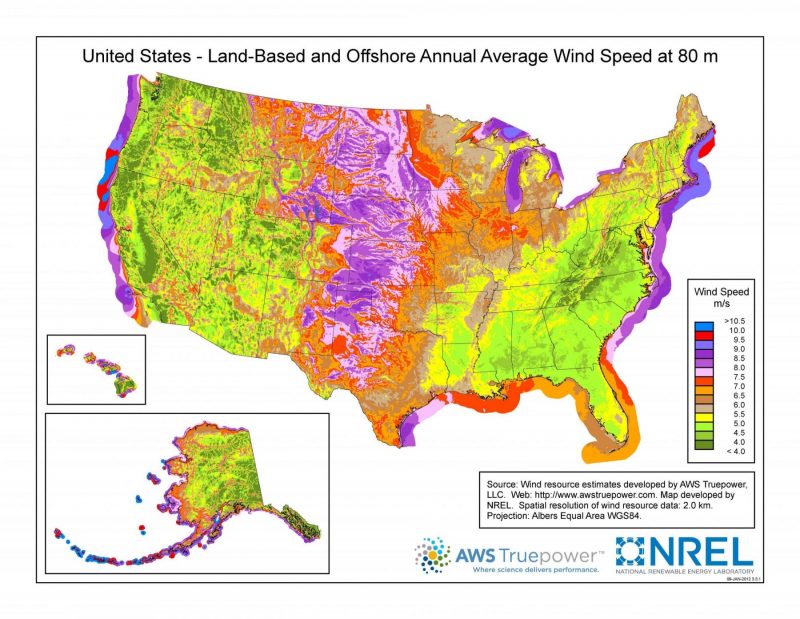
The following maps from the DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory draw the relative availability of renewable free energy resource throughout the The states.
- Wind resources are arable in the Great Plains, Iowa, Minnesota, along the spine of Appalachian Mountains, in the Western Mountains, and many off-shore locations.
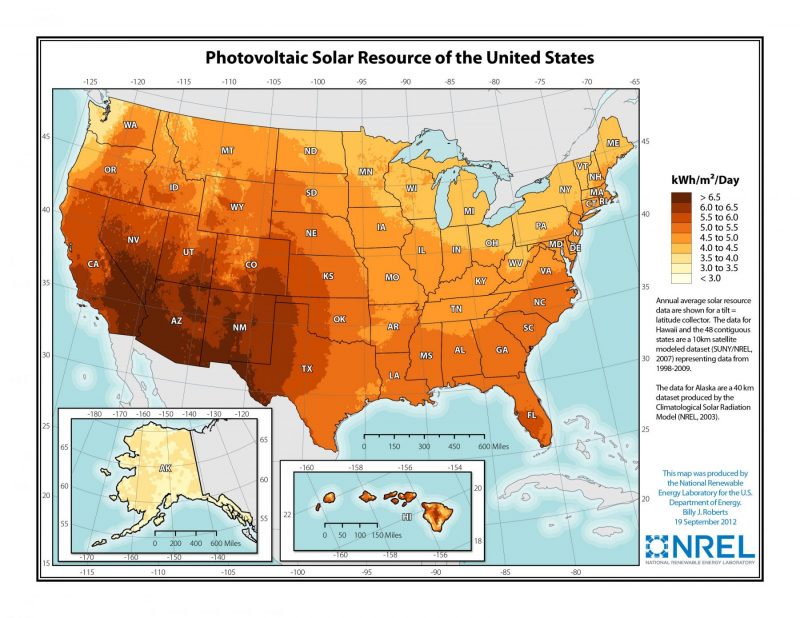
- Solar photovoltaic and concentrating solar power resources are the highest in the desert Southwest and diminish in intensity in a northward direction.
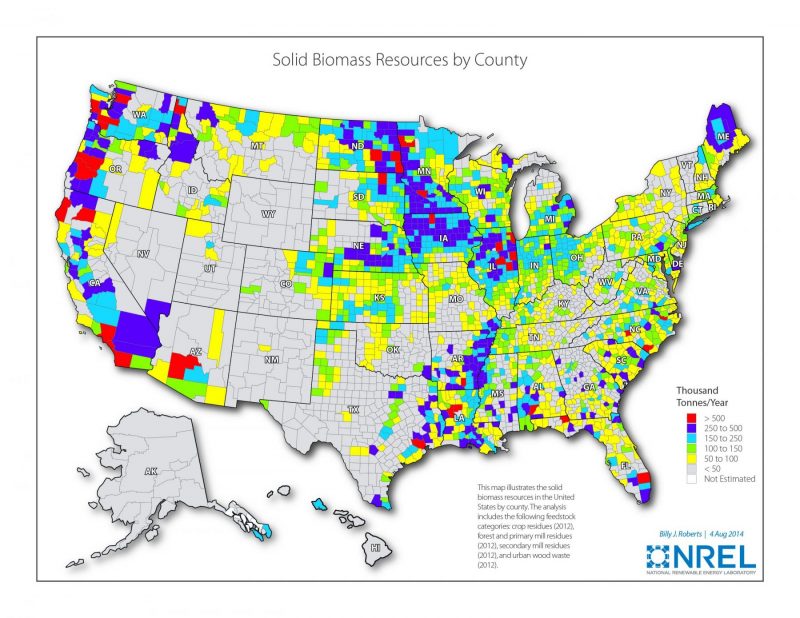
- The best biomass resources are in the upper primal plains (corn) and forests of the Pacific Northwest.
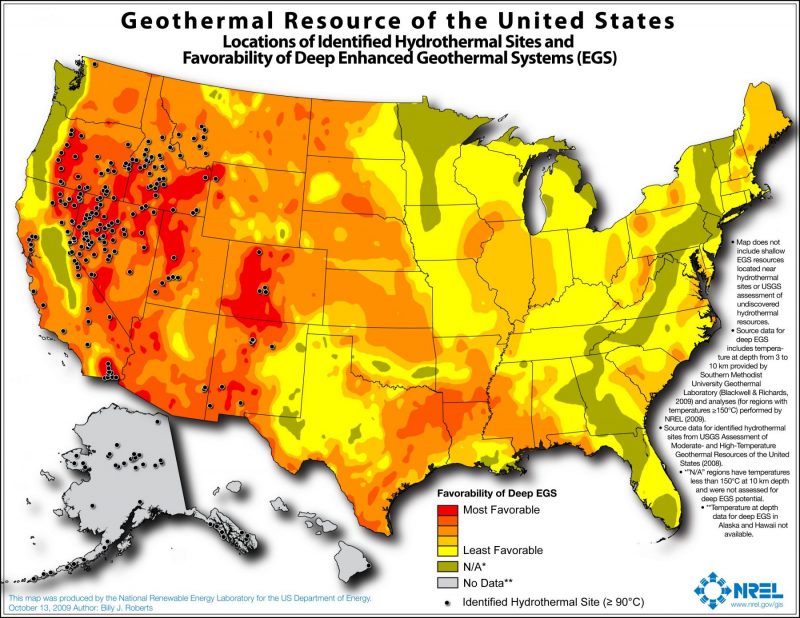
- Traditional geothermal resources are concentrated in the Western United States.
U.Southward. Wind Resources Map
U.Southward. Photovoltaic Solar Resources
U.S. Biomass Resource
U.S. Geothermal Resource
Source: https://www.c2es.org/content/renewable-energy/
0 Response to "what is the world’s leading renewable energy source used to produce electricity?"
Post a Comment